Water on Mars: ESA has discovered three large lakes
 02. 10. 2020
02. 10. 2020

Two years ago, scientists announced discovery of a salt lake under the ice sheet South Pole on Mars. From the beginning, the academic community was very skeptical about this discovery. Now the scientific team has confirmed that the lake really is there - more precisely, that it is a system of at least three lakes.
The discovery was reported on September 28.09.2020, XNUMX in the magazine Nature Astronomy. A satellite was used for the research Mars express operated European Space Agency (ESA). They follow the discovery of a single lake in 2018.
"We were able to identify the same lake as in 2018. In addition, we found three more around it.", said Elena Pettinelli, Scientist for Planetary Research (University of Rome). "It's a very complex system of water bodies."
The team used a probe-based tool to explore Mars' South Pole Mars expresswhich is called Mars Advanced Radar for Subsurface and Ionosphere Sounding (MARSIS) - Advanced Mars radar for subsurface and ionosphere exploration. The signal sent by the radar penetrates a few meters below the flight level and bounces back. According to the reflection characteristics, it is then possible to infer the composition of the material under the ice sheet: eg stone, ice, water… In the same way, underground reservoirs of water, oil, gold deposits, etc. on Earth are sought.
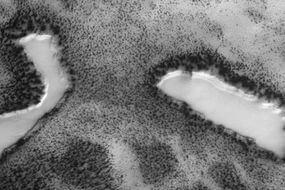
The lakes cover a total area of 75000 km2. The largest of them is 30 km long and is just surrounded by three others, which measure only a few kilometers.
Salt lakes?
Scientists they believethat the low pressure on Mars makes it impossible to keep the water in a liquid state. Nevertheless, they thought that Mars might have underground reservoirs of water as a remnant of when Mars had its own sea and lakes on the surface. If such tanks exist, then it is a suitable place where Martian life could still function today. Scientists draw an analogy on Earth where microbiological life can function in extreme conditions such as the very cold underground lakes of Antakrtida.
Scientists suggest that Mars' lakes could contain high concentrations of salt. Salt could help keep water liquid. The very heat of the planet's core could play a role, but that's not enough, says Elena Pettinelli.
Salt lakes on Mars with a salt concentration 5 times higher than the salinity of seawater on Earth may contain some life forms. However, if the salt concentration is 20 times higher, life in this piglet is no longer possible. At least that's what he thinks scientist John Priscu, specializing in the environment (Montana State University Bozeman). However, his opinion is in direct conflict with current knowledge. Microbiological life forms have been discovered on Earth that can survive in much more extreme conditions: flowing lava, deep ice at the poles, the depths of the oceans with great pressure.
The near future 2021
Three missions are planned for Mars in 2021: At 02.2021, a second vehicle from the workshop should land on Mars NASA this time named as Perseverance (Perseverance). United Arab Emirates they also don't lag behind and send their probe Hope Mars Mission, which should reach the goal at the same time. The third to the party is China (CNSA), which sent tianwen-1. The Chinese probe also carries its own vehicle on board.
Unwanted discoveries
Long before scientific thinking about water, people like Richard C. Hoagland and / or Mike Bara they paused over photographs from Mars, which show the bodies of water with the naked eye. So it's a question of when the scientific community discovers imaginary America...
- RCH: Lakes
- MB: Aqueous surfaces
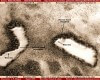
- Water areas?
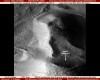
- Water in a rock overhang
- Water in the rock overhang (detail)
- Crowns of trees hundreds of meters high
- Crowns of trees on Mars
- High trees on Mars
recommended literature
In this scientific guide Omniverse brings the author, Alfred Lambremont Webre, stunning replicable evidence of extraterrestrial and extraterrestrial life about intelligent civilizations formed by souls in the afterlife, about super-secret extraterrestrial technology, and about the existence of a secret base and life on Mars.





 1
1